Top investors want consistent returns—without the day-to-day guesswork.
That’s where dividends shine: real companies paying you regular cash.
Imagine each payment compounding until it rivals your salary.
No quick flips, no frantic chart-watching—just predictable growth.
In today’s premium issue, we’re highlighting a four-part dividend strategy that can potentially outpace more traditional buy-and-hold approaches—especially when you factor in reinvested payouts. More importantly, you’ll learn how to apply this framework to accelerate your journey toward financial independence.
By the end of this article, you’ll find my implementation cheat sheet for assembling, automating, and optimizing a dividend-centric portfolio. It’s designed to help you build consistent income over time—and enjoy greater peace of mind along the way.
Who’s a Good Fit for This Portfolio?
Dividend Seekers - Looking for steady cash flow you can count on? Dividend growth ticks that box.
Early Retirement Planners - Want to eventually replace your paycheck with passive income? These payouts can fund your dream lifestyle.
Risk-Conscious Investors - Prefer resilient companies that hold up better in market storms? A diversified dividend strategy can offer that comfort.
Patient Builders - Real wealth takes time—if you’re in for the long haul, consistent dividends can keep you motivated while the market churns.
What Is The Beauty of a Dividend-Growth Approach?
Consistent Income: Dividend-paying companies send me regular checks—no guesswork.
Compound Growth: Reinvesting dividends multiplies my share count over time.
Defensive Strength: Firms with a history of increasing payouts often weather downturns more smoothly.
It’s a steady, time-tested way to build lasting wealth.
This Portfolio’s Core Framework
At the heart of this portfolio is balance.
I break it into four broad categories, each serving a distinct role:
Foundation Dividend Payers
Role: Provide steady, reliable cash flow.
Why It Matters: A backbone that often keeps paying (and sometimes raising) dividends, even in tough markets.
High-Yield Selections
Role: Boost the overall yield.
Why It Matters: Increases your income faster but typically warrants more careful monitoring.
Dividend Growth Leaders
Role: Companies that consistently raise their payouts year after year.
Why It Matters: Fends off inflation, supercharges the compounding effect.
Undervalued Opportunities
Role: Gems are overlooked by the market or traded cheaply.
Why It Matters: Potential for both strong yields and capital appreciation.
This approach diversifies risk across different sectors and yield profiles.
If one segment temporarily falters, the others can keep the dividend stream afloat.
How It Works in Practice
Foundation stocks handle day-to-day reliability.
High-Yield positions give me bigger checks.
Growth picks boost my income potential over time.
Undervalued plays add a possible jolt of upside.
Rebalancing about once a quarter ensures no single category dominates.
I monitor dividend sustainability, fundamentals, and sector exposure to keep the risk balanced and the income growing.
The Compounding Engine
Dividends aren’t just about immediate income.
They’re fuel for compounding:
Reinvest Dividends Automatically: Use Dividend Reinvestment Plans (DRIPs) to buy new shares with each payout.
Watch the Snowball Grow: Over time, more shares earn more dividends, which buys even more shares—a powerful flywheel effect.
Reinvested dividends have historically contributed a large chunk of the stock market’s total return.
It’s a slow-and-steady game, but that’s what builds lasting wealth.
On the topic:
Potential Outcomes & Lifestyle Benefits
Even a modest yield, say around 3–5%, can scale impressively over the years, thanks to regular dividend hikes and reinvestment.
If your portfolio eventually throws off enough income to cover your monthly living expenses - you can step away from the grind.
That’s the financial autonomy we aim to create.
If you’re serious about locking in a steady income and compounding growth, the premium section spells out every detail—specific stocks, precise allocations, and a step-by-step roadmap you can copy.
And to make it even easier, I’m including a quick-reference Cheat Sheet you can pin to your desk—so you’ll always know the key steps and allocations at a glance.
Coming Next:
Exact Stock Picks & Rationale — Know which companies deliver consistent dividends and growth—even in choppy markets.
Allocation Targets — Clear percentage breakdowns for each category, plus the “why” behind them.
Maintenance Checklist — Spot trouble signs early, rebalance on time, and stay on course—no second-guessing.
Projections & Case Studies — See how this strategy can accelerate your journey to early retirement with real-world examples.
One private client I worked with replaced half their paycheck with dividend income in just six years—no fancy market timing required.
Ready to step up your game? I’ve got every detail waiting.
Advanced Picks, Allocations & Implementation
Below, I detail exactly which stocks I hold up as prime examples, why they made the cut, and how to manage them.
A. Handpick the Stocks: The “What” and the “Why”
Below is my personal illustration.
Not a guarantee of success, but a tried-and-true framework you can adapt. I’m grouping them into four buckets, with the reasoning behind each choice.
1. Core Dividend Pillars (50%)
Purpose: These are your foundation—the stocks that have historically weathered multiple market cycles while steadily paying and often raising dividends.
PepsiCo (PEP)
Why? Global snack-and-beverage giant, over 50 consecutive years of annual dividend hikes. Low volatility relative to the broader market.
Key Metrics: Historically, Pepsi’s dividend payout ratio (dividends ÷ earnings) has stayed in a comfortable zone, meaning they’re unlikely to cut the dividend even in tough times.
Realty Income (O)
Why? Self-branded as the “monthly dividend company,” so you get monthly payouts—great for compounding and cash-flow management.
Key Metrics: Runs a diverse real estate portfolio with high occupancy rates, which supports reliable distributions. Look at Funds from Operations (FFO) coverage rather than traditional EPS.
Merck (MRK)
Why? Defensive healthcare major. Pharmaceutical demand is less cyclical. If the economy tanks, people still need medication.
Key Metrics: Consistent R&D investment, a track record of stable earnings, and a decent dividend growth streak. Keep an eye on patent expirations, but historically they’ve navigated those with a solid pipeline.
2. High-Yield Boosters (20%)
Purpose: Increase overall yield. These picks may be more susceptible to price swings or sector fluctuations, but they’re selected for relatively steady track records in paying higher dividends.
Exxon Mobil (XOM)
Why? An energy powerhouse; while the oil sector can be volatile, XOM has proven its commitment to shareholder payouts.
Key Metrics: Look at the dividend coverage during down oil-price cycles. Exxon’s integrated business model (upstream, downstream, chemicals) can smooth out revenue bumps. Be prepared for some price fluctuations with energy stocks.
TotalEnergies (TTE)
Why? A global energy company aiming to diversify into renewables, plus offering a higher-than-average yield.
Key Metrics: Keep an eye on the payout ratio, strategic moves into LNG and renewable projects, and overall balance sheet strength. High yields can sometimes indicate higher risk, but TTE’s global footprint gives a degree of resilience.
3. Dividend Growth Drivers (20%)
Purpose: Maintain a growing dividend stream. These may not offer huge yields today, but they tend to raise payouts consistently.
United Parcel Service (UPS)
Why? Logistic juggernaut with strong pricing power—especially in the e-commerce era. They’ve raised dividends for years, often beating inflation.
Key Metrics: Check operating margins and the ratio of CapEx to free cash flow. If e-commerce trends remain strong, UPS can keep boosting its dividend.
AbbVie (ABBV)
Why? The pharmaceutical firm is known for robust shareholder returns and a history of dividend growth.
Key Metrics: Pipeline diversity is crucial—monitor how they replace revenue from older drugs. Historically, AbbVie’s management has shown a willingness to reward shareholders with dividend hikes but stay alert to R&D success rates.
4. Undervalued Prospects (10%)
Purpose: Add smaller, potentially overlooked companies that might offer outsized returns and respectable dividend yields but require extra diligence.
Deluxe Corporation (DLX)
Why? Legacy printing and check services, branching into digital marketing solutions. Often trades at lower valuations, which can mean higher yields.
Key Metrics: Watch revenue trends as checks and printing can be declining industries. The pivot to marketing could take time, but if managed well, you might enjoy both a decent yield and capital appreciation.
Entravision (EVC)
Why? Smaller media/marketing companies pay a very high dividend yield. This can boost overall portfolio income but brings more risk.
Key Metrics: Verify that the payout ratio is sustainable and track how their digital ad segments are performing. High yield sometimes hints at underlying trouble, so it demands more frequent reviews.
B. Suggested Allocation & Nuanced Projections
Estimated Dividend Yield: ~3–5% blended.
Real-World Outcome: On a $100,000 portfolio, you might collect around $4,000 a year initially. Over the next decade, if these companies keep hiking dividends, your yield on cost could rise significantly—potentially reaching 6–8% on your original investment.
Historical Snapshots:
PepsiCo raised its dividend for over 50 years, often in the high single-digit percentage range annually.
Realty Income typically notches annual dividend raises.
Energy Stocks like XOM have had rough patches but historically remain firm about maintaining or increasing their dividend, even during commodity slumps.
UPS & AbbVie have delivered strong dividend CAGR (Compound Annual Growth Rate) over the past few years.
Risk Balancer: Diversifying across sectors—consumer staples, real estate, healthcare, energy, logistics—reduces the impact if one sector experiences a downturn.
C. Rebalancing & Advanced Maintenance
Quarterly or Semi-Annual Review
Step A: Look at each holding’s payout ratio (dividends ÷ earnings or, for REITs, dividends ÷ FFO) to ensure dividends remain covered.
Step B: Evaluate the growth trajectory. If a company’s future pipeline or business model is faltering, be ready to pivot.
Manage Sector Concentration
Energy can be a roller coaster if oil prices dip. You might trim your energy positions to stay near 20% if your energy positions balloon.
Valuation Checks
Even a great company can become overpriced. If a stock’s price soars well above fair valuation, you might funnel partial gains into a lagging (but still fundamentally strong) holding.
Historical Proof: In major downturns, rebalancing ensures you “buy low” on high-quality names with unshaken fundamentals. Over the long run, that translates to higher returns and compounding yields.
D. Implementation Checklist: More Detail, Step by Step
You now have a practical outline:
Specific categories (core, high-yield, growth, undervalued)
Concrete examples of stocks to consider
Exact allocation suggestions
Before making any moves, consider your own financial goals and risk tolerance. No single approach fits everyone, and every investment carries its own risks. Still, many have found that a careful dividend-focused strategy can serve as a powerful engine for compounding.
If you decide to pursue this path, a year from now you could be glad you planted these seeds. In a decade, you might look back and see it as a significant step toward greater financial freedom. Personally, I value dividends for their consistency and growth potential, and I hope these insights help you develop a plan that works for you.
Remember: this information is for educational purposes and is not financial advice. Always do your own research—or consult a professional—before committing capital. Ultimately, the decision to build or adjust your portfolio is yours alone.
Good luck on your investment journey!
- Mike






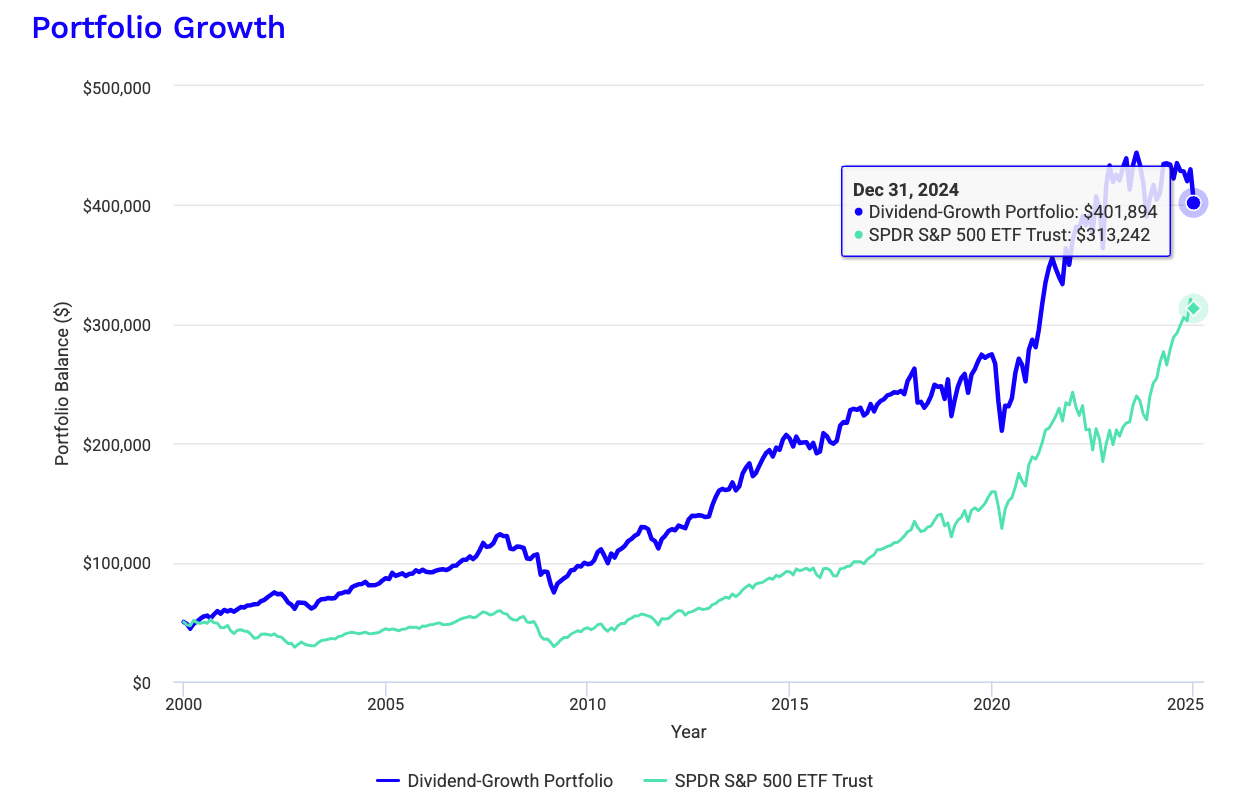
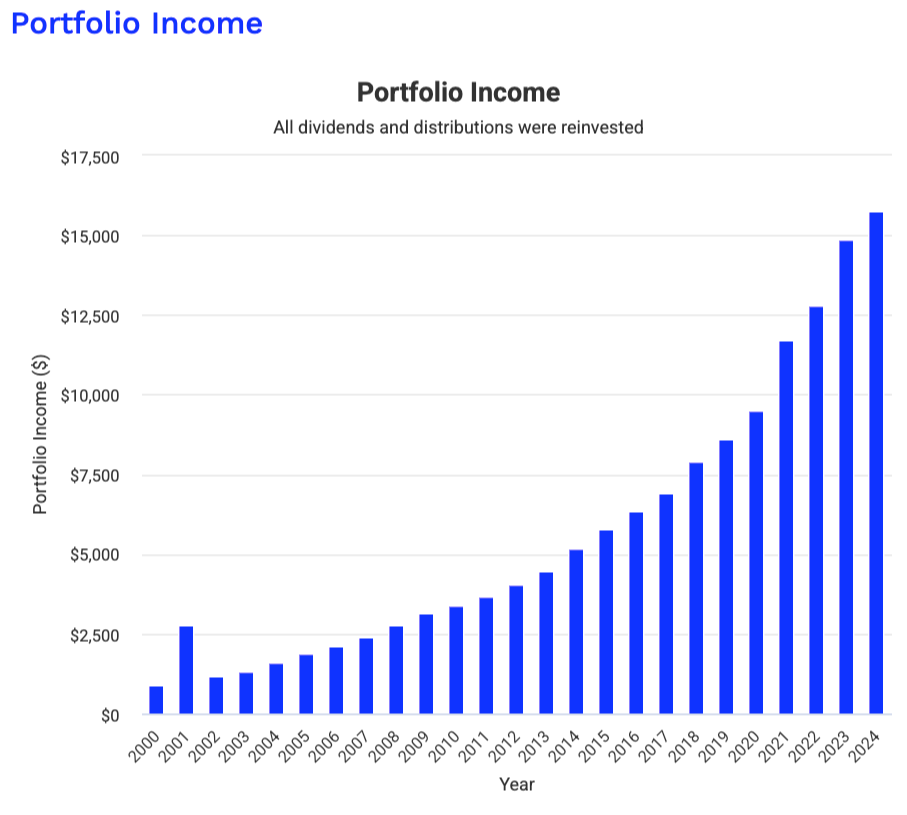

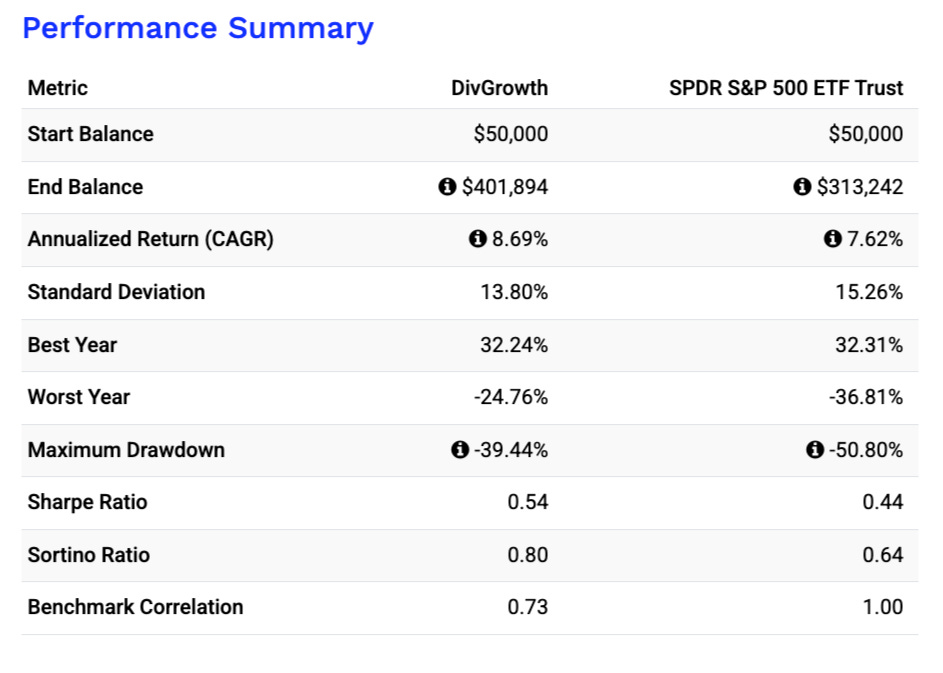





Twenty years in markets taught me: dividends are like psychological anchors that keep you invested when others panic. The beauty of your four-bucket system is how it balances immediate yield against future growth. Solid framework.